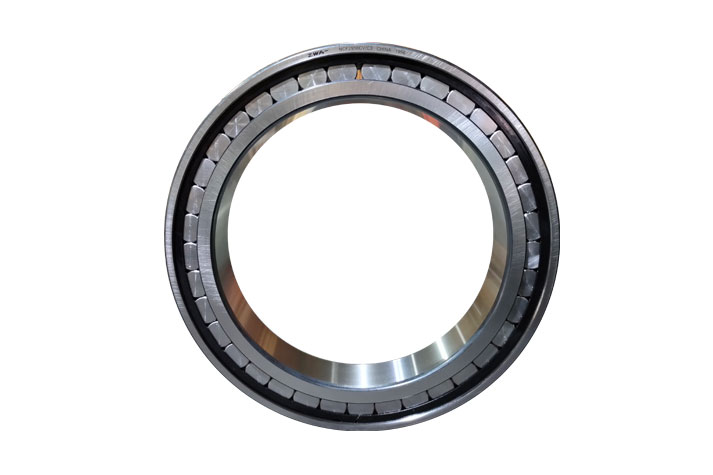
Bearings are divided into two main categories, of which there are several types. The rolling bearings are first introduced. The classification of rolling bearings is mainly based on the shape of rolling element, load-bearing force and structural pattern. The rolling bearing is generally composed of inner race, outer race, rolling element and holder.
1. Classification based on the structure of rolling bearings
According to the load direction or nominal contact angle that the bearing can bear, it can be divided into:
(1) Radial bearing--mainly used to bear radial load, with nominal contact angle ranging from 0 to 45. Based on the nominal contact angle, types of radial ball bearing can be divided into radial contact bearing with nominal contact angle 0 and centrifugal contact bearing whose nominal contact angle is over 0 and less than 45.
(2) Thrust bearing--mainly used for bearing axial load, with nominal contact angle ranging from 45 to 90. According to the nominal contact angle, thrust bearings can be divided into axial contact bearing with nominal contact angle 90 and thrust angular contact bearing whose nominal contact angle is more than 45 but less than 90.
2. Classification based on the types of rolling elements
(1) Ball bearing types--the rolling element is a ball.
(2) Roller bearing--the rolling element is a roller. According to the types of rollers, roller bearings can be divided into cylindrical roller bearings, in which the roller is cylindrical, and the ratio of length to diameter of cylindrical roller is less than or equal to 3; needle-roller bearings, in which the rolling element is needle roller, and the ratio of length to diameter is more than 3 while the diameter is less than or equal to 5mm; tapered roller bearings, in which the rolling elements are conical; and self-aligning roller bearings that the rolling elements is spherical.
3. Classification based on whether it can self-align
(1) Self aligning bearing--the raceway is spherical, which can adapt to the angular deviation between two raceway axes and angular movement;
(2) Non self-aligning bearing (rigid bearing)---it can resist the angular deviation of the axis line between raceways.
4. Classification based on number of columns for the rollers
(1) Single-row bearing--bearing with a row of rolling elements.
(2) Double-row bearing--bearing with two rows of rolling elements.
(3) Multi-column bearing--bearing with more than two rows of rolling elements, such as three-row bearing, and four-row bearing.
(4) Classification based on whether its components can be separated
Separable bearing--bearing with detachable parts.
Inseparable bearing--the bearing whose ring cannot be separated freely after matching.
(5) Bearings can be classified into several types according to structural shapes, e.g. filling groove, inner and outer rings, the shape of ferrule, structure of side guards, holder, etc.
5. Classification based on the size of the rolling bearing:
(1) Miniature bearing--bearing with nominal outer diameter less than 26mm.
(2) Small bearing--bearing with nominal outer diameter of 28-55mm.
(3) Small and medium-sized bearing--bearing with nominal outer diameter of 60-115mm.
(4) Medium and large bearing--bearing with nominal outer diameter of 120-190mm.
(5) Large bearing--bearing with nominal outer diameter of 200-430mm.
(6) Oversize bearing--bearing with nominal outer diameter over 440mm.